Address
Unit 302, Tower 1, Assotech Business Cresterra, Sector 135 Noida 201301 (UP), India.
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 9:30AM - 6:30PM
Address
Unit 302, Tower 1, Assotech Business Cresterra, Sector 135 Noida 201301 (UP), India.
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 9:30AM - 6:30PM
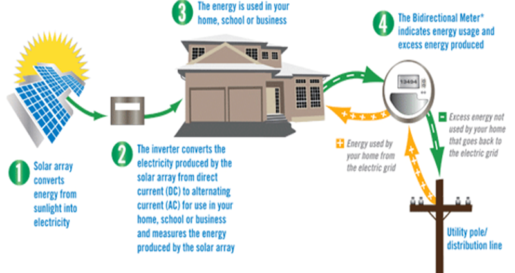
1.
Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it to DC electricity
2.
Your solar system converts that energy to an AC current that can power your home
3.
Energy you don’t use goes back to the utility grid and creates an electricity “credit” for you
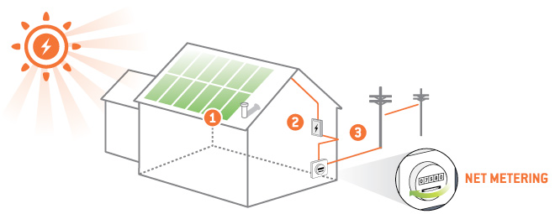
Solar panels convert sunlight into clean, efficient energy that can power your home year round. When the sun shines, the electricity travels from the panels through wires into a piece of equipment called an inverter. An inverter converts the type of electricity produced by the panels (called Direct Current, or DC) into the type of power your house uses (called Alternating Current, or AC). Once the electricity goes through the inverter, it travels into your home’s electrical panel. At night, when your panels are not generating electricity, you continue to get electricity from the local utility. But during the day, your solar panels can produce more power than you consume, feeding power into the utility grid, supplying clean electricity to your community and spinning your meter backward.


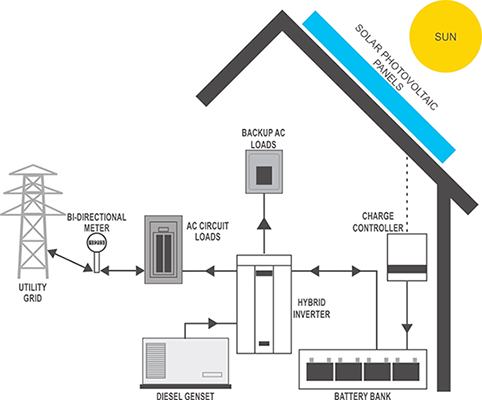
The "Grid-Tie With Battery Backup or Hybrid" PV system incorporates one or more special AC circuits that are not directly connected to the electric grid like the rest of the building, but are always powered through the inverter and/or charge controller. These circuits may power a refrigerator, selected lights, computers or servers i.e. any devices the owner deems essential. The "dual function" inverter can supply the utility grid with any excess power produced by the system like the "grid-tie" inverter, plus the inverter works with the PV modules and battery bank (through the charge controller) to provide AC power to the backup circuits when the grid is down. The charge controller manages the battery voltage, keeping them fully charged when the grid is live, and preventing them from being depleted when the system is drawing power from them.
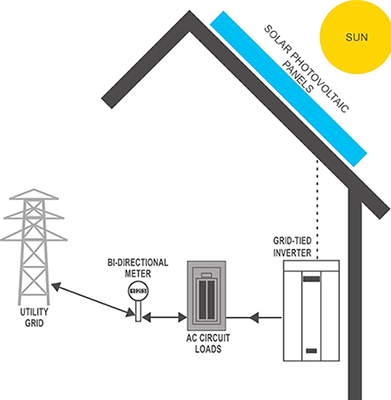
There are no batteries to store excess power generated--the electric utility essentially stores it for you through a system called "net-metering." DC (direct current) generated by the PV panels is converted into AC (alternating current) power by the inverter. Output from the inverter is connected to your existing distribution panel (breaker panel) that feeds the rest of your site. During periods when your grid-tie system is generating even more energy than your site requires, any excess is fed back into the grid for others to use and the electric utility company "buys" it from you. They provide credits to your account for all the power that is pushed back into the grid through the meter. And your meter will literally run backwards! When your site needs to draw more energy than it is producing (say, during cloudy conditions or at night), electricity is provided by the power grid in the normal manner.
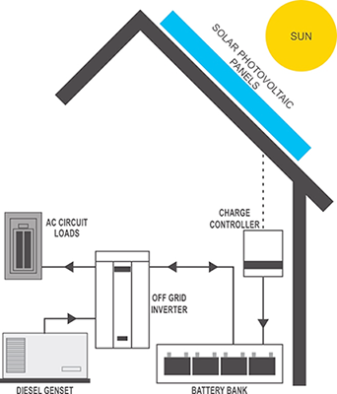
The Off-Grid or Stand-Alone PV System incorporates large amounts of battery storage to provide power for a certain number of days (and nights) in a row when sun is not available. The array of solar panels must be large enough to power all energy needs at the site and recharge the batteries at the same time. A diesel generator is often employed for emergency backup power.
The area required for a 1 kW power plant setup is around 10 sq. meters or 100 sq. feet. Furthermore, for 1MW Solar PV plant area required is 4.5-5 acres for crystalline technology and around 6.5-7.5 acres for thin-film technology. This is only a rough benchmark and may vary based on technology and efficiency of panels.
The useful life of a typical Solar Power Plant is considered to be 25 years. This is the duration for which long-term PPAs are signed and financial models are built. However, Solar Power plants can run beyond 25 years while producing a lower output. Many Solar Panel manufacturers guarantee an output of 90% at the end of 10 years and 80% at the end of 25 years.
The usual benchmark for energy generated from a 1kW Solar Power Plant is considered as 1400-1500 units, which translates to around 1.5 million units for a 1MW plant. This is only a benchmark and should not be considered as the actual output for a given location. The amount of actual energy generated from a Solar Power Plant in a year depends on both internal and external factors. External factors that are beyond the control of a solar developer can include the following:
The output also depends on the following internal factors all of which are within the control of a Solar Developer:
The various modes under which a Solar Power plant can be setup depend on the specific requirement. All the following are valid modes and the costs for each kind of system varies based on various factors:
Rooftop Solar Power plants can be broadly categorized into Battery-based and Non-Battery based systems. The downward revision of these costs has led us to provide our clients with extremely competitive quotes for their Solar PV Systems. More details can be accessed on the following MNRE Download here
Based on these factors, our sales engineers can perform a site assessment to design an optimum Solar PV Solution for you.
There are 2 kinds of Financing mechanisms that are usually discussed – Recourse Financing and Non-Recourse Financing. Recourse Financing requires collaterals and other extensive guarantees from the Solar Developer who wishes to avail loan. Non-Recourse Financing, on the other hand, does not require any additional collateral, as the Asset or Power Plant itself is the collateral in this case. Recourse Financing is the prevalent mechanism in India currently owing to lack of confidence of banks in the Power and Solar Power sector. The typical Debt-Equity Ratio (Loan to Investment Ratio) for Solar Power plants is 70:30. And the typical collaterals required for a 70% project cost loan could be in the range of 40-60% project cost. This, however, varies from bank to bank as each bank has its own risk perception/mitigation strategy, exposure targets to various sectors and Non-Performing Asset (NPA) limits.
Subsidy is not available for Grid Connected plants that engage in sale of power either to the local DISCOM or a 3rd party. Following are the benefits a Solar Power Developer involved in Sale of Power Generated can avail:
Yes. Accelerated Depreciation benefits can be claimed by Off-Grid and Grid-Connected Solar Power Developers in order to offset taxes on profits from their connected businesses. Typically, 90% depreciation is allowed with 80% allowed in the first year.
We believe that the following points should form the basis for selection criteria of a Solar EPC Provider by a client:
Net Metering is a billing mechanism that credits solar energy system owners for the electricity they add to the utility grid. For example, if a residential/commercial customer has a Solar PV System on his rooftop, it may generate more electricity than required for captive consumption. This extra electricity will flow back to the utility grid and the customer will get compensated for the same. This is made possible by use of a bi-directional meter which will turn backwards when a customer adds extra electricity to the grid. Indian states of Delhi, Haryana, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Gujarat, Kerala, Punjab and Andhra Pradesh have started implementation of net/gross metering, and the policy has been announced by the respective state electricity boards. Feasibility study will be done by the electricity boards, and after inspection the existing meters will be replaced by bidirectional meters. Applications are taken up on a first-come-first-serve basis and technical feasibility.